Wednesday, May 20, 2020
Neo-Darwinsm: a philosophy with no supporting scientific proof
All hail the cult of Science and bow down to the altar of Chuckie
by StFerdIII
Edited from Source
Neo-Darwinism was disproven (yet again), long ago in 2003 by 3 evolutionary believers (called scientists), in Spain. Not that the Fake News-Fake Science circus would divulge such information. Experiments, observations, reality which contravenes the Secular Religion of Darwinism-Evolution is studiously ignored, if not pilloried and calumnied. Neo-Darwinism is a philosophical reflection, not a science.
The study performed at the Institut Cavanilles de Biodiversitat i Biologia Evolutiva, Universitat de Valencia in Spain, was published in PNAS (i.e., 10/26/2003), and it found no support for the central tenets of neo-Darwinian theory: namely, that evolutionary adaptations arise by natural selection acting on beneficial mutations.
Neo-Darwinism, also termed the modern synthesis of evolutionary biology, was formulated in the 1940s to rescue Darwin’s views on natural selection from growing theoretical problems. It incorporated the necessity of genetic mutations to provide the raw material for variation on which natural selection acts. This revision was necessary when the rediscovery of Mendel’s laws of inheritance ruled out ideas of blending inheritance, showing instead that inherited characters were based on discrete entities (genes) that were passed on unaltered to the offspring.
To test neo-Darwinian evolution in a microcosm, Rafael Sanjuán, Andrés Moya, and Santiago F. Elena worked with RNA viruses: organisms with a small, compact genomes that should respond quickly and noticeably to mutations. The team was looking for epistatic interactions: i.e., the effects of multiple independent (non-allelic) mutations on each other, rather than the effects of single mutations alone.
These interactions can be antagonistic or synergistic: they can work against one another or with one another. Epistasis is defined as “any interaction of nonallelic genes, especially the suppression by one gene of the effect of a nonallelic gene.” Of note in this paper are the opening lines in the abstract that tell how rarely this important concept has been studied before (this is science-speak for never):
The tendency for genetic architectures to exhibit epistasis among mutations plays a central role in the modern synthesis of evolutionary biology and in theoretical descriptions of many evolutionary processes. Nevertheless, few studies unquestionably show whether, and how, mutations typically interact. Beneficial mutations are especially difficult to identify because of their scarcity. Consequently, epistasis among pairs of this important class of mutations has, to our knowledge, never before been explored.
Let’s picture a 2×2 grid. On the left side, label the rows “beneficial” and “deleterious.” On the top, label the columns “synergistic” and “antagonistic.” Now put two dots in each box, with the dots representing mutations that will interact with one another.
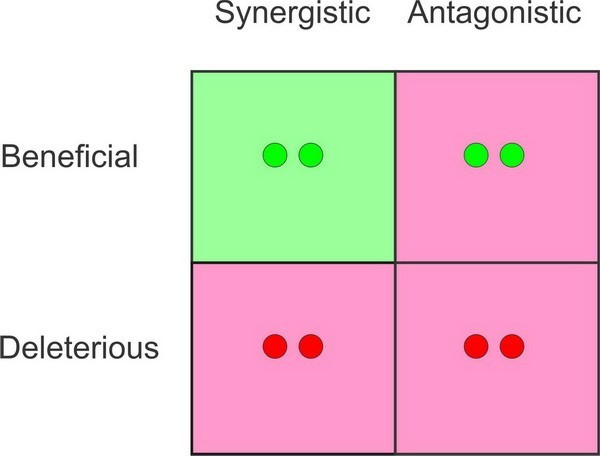
The Spanish team performed two classes of experiments to measure the effects of epistasis on mutations and they did not find a single example of beneficial and synergistic mutations.
The researchers found that beneficial mutations do not add up, even in the best of circumstances.
Neo-Darwinian theory assumes that beneficial mutations act independently, but the team found that of the eight actual best-case scenarios (two beneficial mutations working antagonistically, since none worked synergistically) over half decreased the total fitness of the result from what would be expected if the beneficial mutations acted alone.
In conclusion, they caution evolutionary modelers to realize that they can no longer merely assume fitness gains (if any) add up.
In other words, there is no single scientific proof to support fish to fishermen, bacteria to bats, and hyenas to humans.